Open Bw-Tree Benchmark 분석
Open Bw Treed Benchmark 코드 흐름 따라가면서 파악하기.
- basic_test.cpp
- Operations
- Performance Evaluation
- Building a Bw-Tree Takes More Than Just Buzz Words
- 참고자료
basic_test.cpp
간단한 insert/delete/read op.을 실행하여 correctness 확인
Operations
Insert
bool Insert(const KeyType &key, const ValueType &value);
키가 이미 존재하면 false 리턴, CAS 실패시 성공할때까지 반복(while(1))
현재 epoch에 추가
EpochNode *epoch_node_p = epoch_manager.JoinEpoch();key를 통해 Context 생성
Context context{key} class Context { const KeyType search_key = key; NodeSnapshot current_snapshot; NodeSnapshot parent_snapshot; }Traverse를 통해 키가 존재하는지 확인. 없으면 마지막 snapshot을 가져옴.
const KeyValuePair *item_p = Traverse(&context, &value, &index_pair); NodeSnapshot *snapshot_p = GetLatestNodeSnapshot(&context);CAS 실행에 필요한 변수들 생성
const BaseNode *node_p = snapshot_p->node_p; NodeID node_id = snapshot_p->node_id; const LeafInsertNode *insert_node_p = \ LeafInlineAllocateOfType(LeafInsertNode, node_p, key, value, node_p, index_pair);CAS 실행
bool ret = InstallNodeToReplace(node_id, insert_node_p, node_p);성공할시 epoch 에서 나감
epoch_manager.LeaveEpoch(epoch_node_p);
Delete
bool Delete(const KeyType &key, const ValueType &value);
key-value pair가 존재하지 않으면 false 리턴
Insert와 매우 유사한 구조를 지님.
현재 epoch에 추가
EpochNode *epoch_node_p = epoch_manager.JoinEpoch();key를 통해 Context 생성
Context context{key} class Context { const KeyType search_key = key; NodeSnapshot current_snapshot; NodeSnapshot parent_snapshot; }Traverse를 통해 키가 존재하는지 확인. 없으면 false 리턴하고 종료.
const KeyValuePair *item_p = Traverse(&context, &value, &index_pair); NodeSnapshot *snapshot_p = GetLatestNodeSnapshot(&context);CAS 실행에 필요한 변수들 생성
const BaseNode *node_p = snapshot_p->node_p; NodeID node_id = snapshot_p->node_id; const LeafDeleteNode *insert_node_p = \ LeafInlineAllocateOfType(LeafDeleteNode, node_p, key, value, node_p, index_pair);CAS 실행
bool ret = InstallNodeToReplace(node_id, delete_node_p, node_p);성공할시 epoch 에서 나감
epoch_manager.LeaveEpoch(epoch_node_p);
GetValue
두가지 함수 원형 존재
void GetValue(const KeyType &search_key, std::vector<ValueType> &value_list);
ValueSet GetValue(const KeyType &search_key)
둘의 차이는 value_list 벡터를 생성한 이후 그대로 참조자를 통해 접근하느냐, 혹은 unordered_set을 사용해 리턴하느냐의 차이.
현재 epoch에 추가
EpochNode *epoch_node_p = epoch_manager.JoinEpoch();TraverseReadOptimized() 함수를 통해 value_list 생성
Context context{search_key}; TraverseReadOptimized(&context, &value_list); -> LoadNodeIDReadOptimized -> TakeNodeSnapshotReadOptimized & FinishPartialSMOReadOptimizedwhile(1) 돌면서 leafNode 찾기
while(1) { child_node_id = NavigateInnerNode(context_p); LoadNodeIDReadOptimized(child_node_id, context_p); NodeSnapshot *snapshot_p = GetLatestNodeSnapshot(context_p); if(snapshot_p->IsLeaf() == true) { NavigateLeafNode(context_p, *value_list_p); return } }
Performance Evaluation
The Bw-Tree: A B-tree for New Hardware Platforms
Environment
Win32 native InterlockedCompareExchange64 to perform CAS default page size of 8K
Machine
Intel Xeon W3550 (at 3.07GHz) with 8 hyper thread logical cores + 24GB RAM
Evaluation Datasets
- Xbox LIVE Key: 94 bytes values: averaging 1200 bytes workload: 27 Million get-set operations read-to write ratio: 7.5 to 1
- Storage deduplication trace Key: 20-byte SHA-1 hash values: 44-byte metadata string workload: total 27 Million, 12 Mullion unique chunks. read-to-write ratio: 2.2 to 1
- Synthetic Key: 8-byte integer values: 8-byte integer workload: 42 Million operations read-to-write ration: 5 to 1
Results
LATCH-FREE DELTA UPDATE FAILURES
| Failed Splits | Failed Consolidation | Failed Updates | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xbox | 1.27% | 0.22% | 0.0171% |
| Dedup | 0.25% | 1.19% | 0.0013% |
| Synthetic | 8.88% | 7.35% | 0.0003% |
Failed Updates: extremely low. Failed Splits & Consolidation : larger than update because they must compete with the faster record update operations. Synthetic: extremely small record leads to faster update. Which ultimately leads to high probability of failure.
Delta Chain Length
Small delta chain length == frequent consolidation Best at 4~8 length. 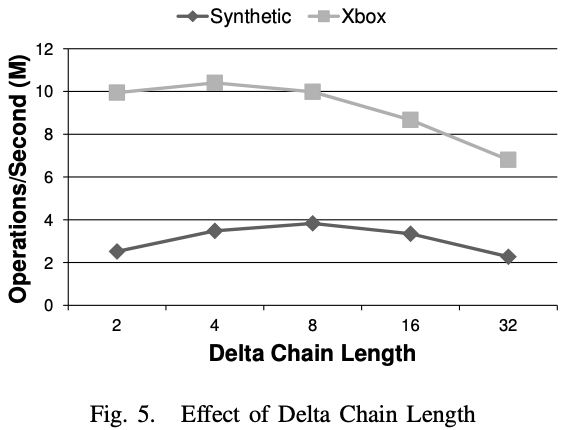
Cache Performance
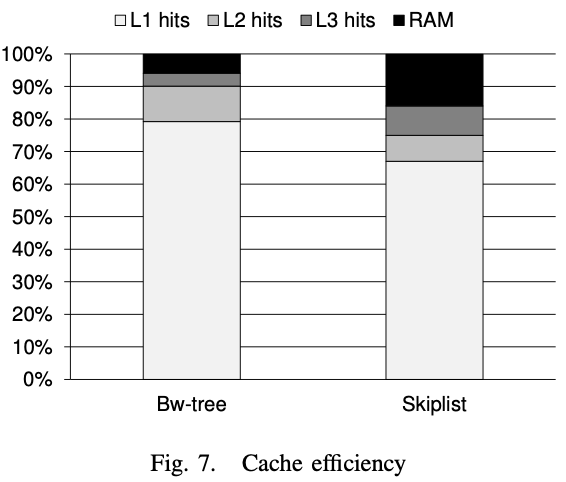
Prime Reason for high L1 cache hit: search efficiency
Suggestions
Tuning search performance using a cache sensitive page search technique. [23] S. Chen, P. B. Gibbons, T. C. Mowry, and G. Valentin, “Fractal Prefetching B±Trees: Optimizing Both Cache and Disk Performance,” in SIGMOD, 2002, pp. 157–168. [24] D. B. Lomet, “The Evolution of Effective B-tree: Page Organization and Techniques: A Personal Account,” SIGMOD Record, vol. 30, no. 3, pp. 64–69, 2001.
Building a Bw-Tree Takes More Than Just Buzz Words
Environment
g++ (v5.4) with tcmalloc
Machine
two Intel Xeon E5-2680 v2 CPUs (10 threads with 2x HT) + 128 GB RAM
Evaluation Datasets
Yahoo! Cloud Serving Benchmark microbenchmark A (Read/Update 50/50) C(Read-only) E(Scan/Insert 95/5) three key types 52 Million keys for 64-bit random integers / 64-bit monotonically increasing integers 27 Million keys for email addresses(32-byte)
Pre-allocation
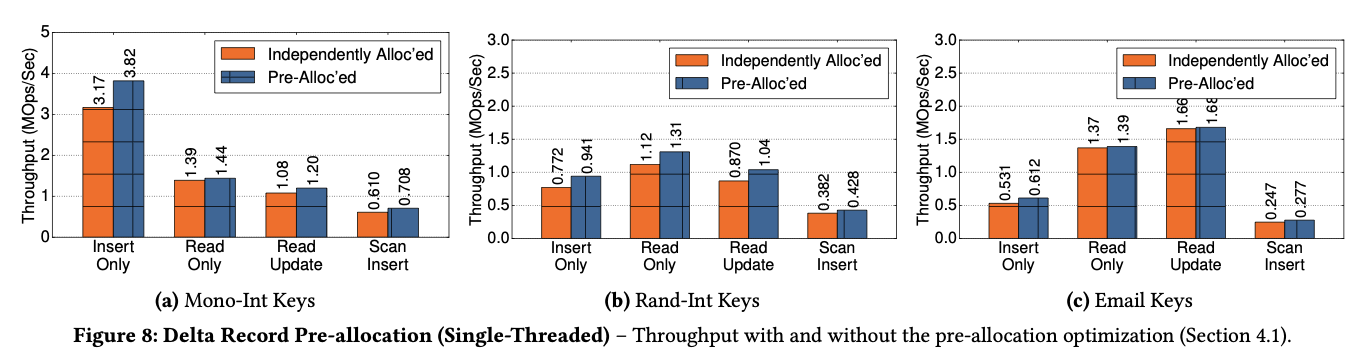
- better locality
- reduces the number of small memory allocations
- wasted memory space
Fast Consolidation & Search Shortcuts
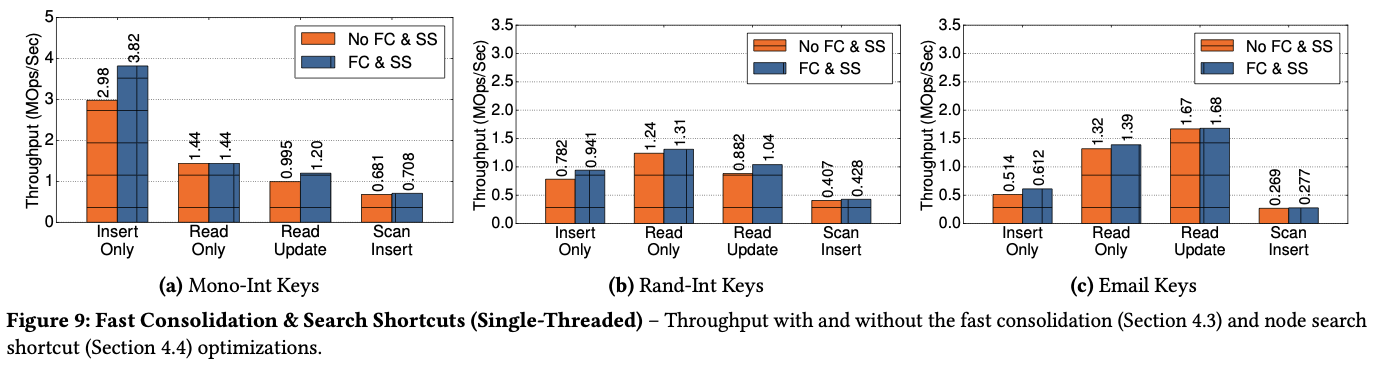
- reduce consolidation time
- search optimization improves the performance of random lookups
Delta Chain Length
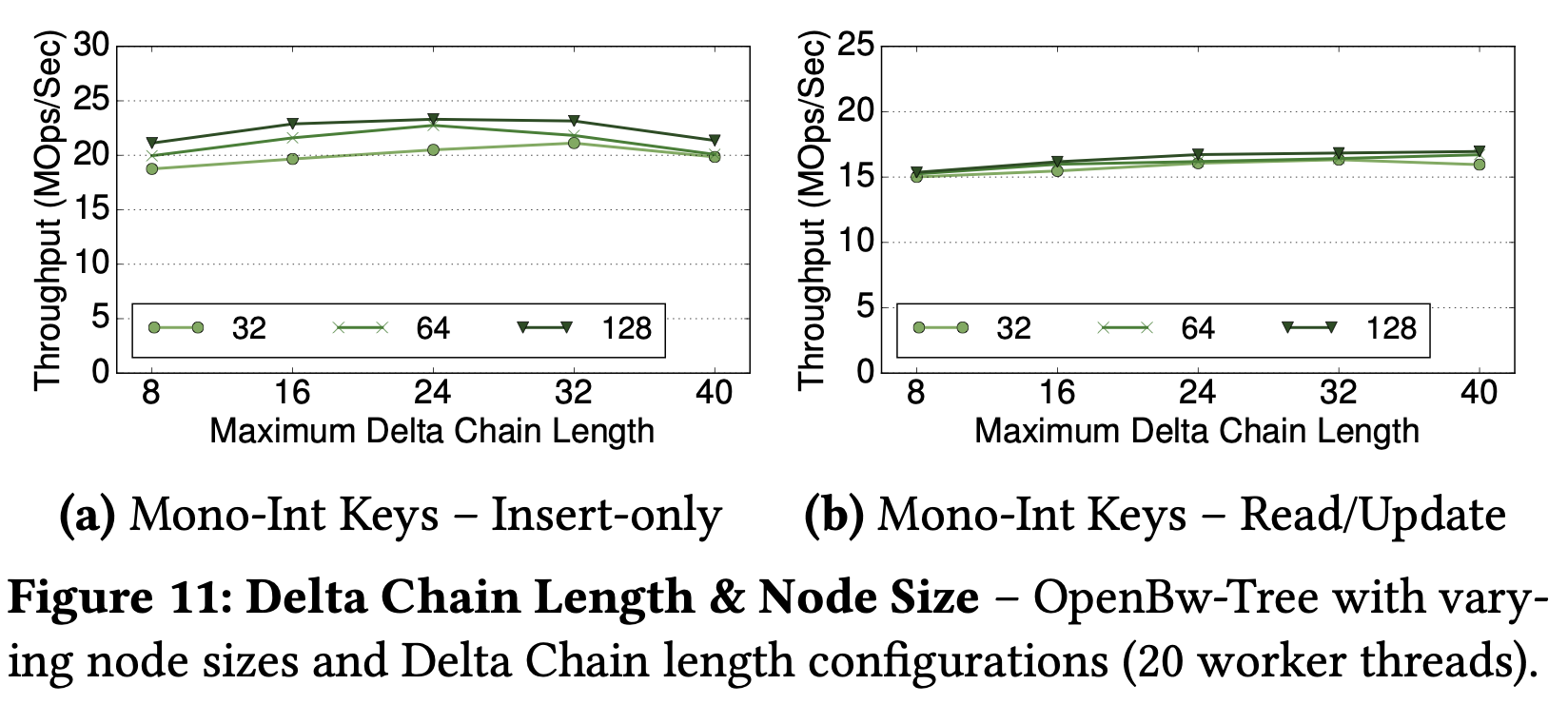
- best at node size 32 / chain length threshold 40
- larger node is favored because shallow tree results in fewer cache misses than a deeper three with smaller nodes. & no frequent cache line invalidation during insert thanks to the delta chain.
Results
It is suggested by the results that the optimal Delta Chain length threshold is between 16 and 24 for both Insert-only and Read/Update workloads. We believe the difference on optimal Delta Chain lengths is related to the pre-allocation optimization, because it reduces the overhead of delta chain traversal. Furthermore, the type of keys also has an effect on the optimal threshold. For Email Insert-only workloads on OpenBw-Tree, the optimal Delta Chain length threshold is between 16–24, while for Read/Update workloads it is 32–40.
참고자료
The Bw-Tree: A B-tree for New Hardware Platforms
Building a Bw-Tree Takes More Than Just Buzz Words
